INTRODUCTION
The contamination of crops with mycotoxins is a major worldwide challenge in livestock production. Ergot alkaloids are mycotoxins mainly produced by fungal Claviceps species that usually affect cereals and can cause adverse health effects in animals, standing out their neurotoxic effects. Fumonisins and aflatoxins are generated by other mycotoxin-producing fungi, contaminating cereals. Sterigmatocystin (STC) is a precursor for the synthesis of aflatoxin B1 and has been associated with several toxic effects, such as hepatotoxicity, nephrotoxicity and pulmonary injuries.
OBJECTIVE
The aim of this study was to evaluate the in vitro efficacy and the selectivity (no adsorption of vitamins or amino acids) of an anti-mycotoxins agent based on selected binding material combined with natural extracts and yeasts.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
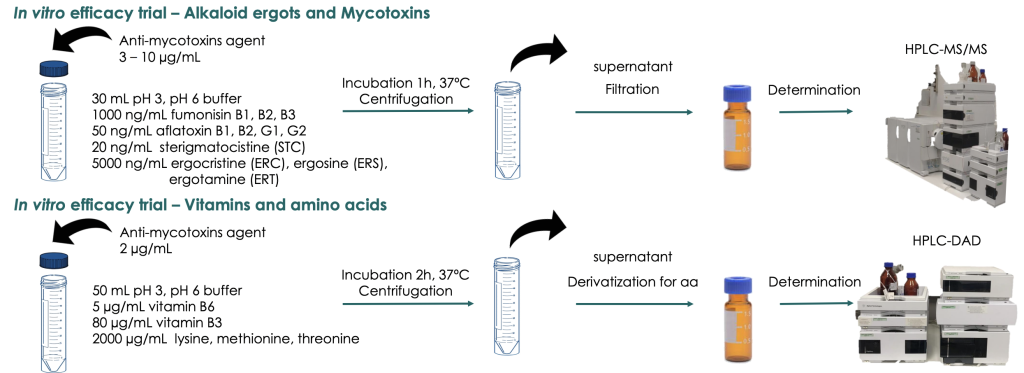
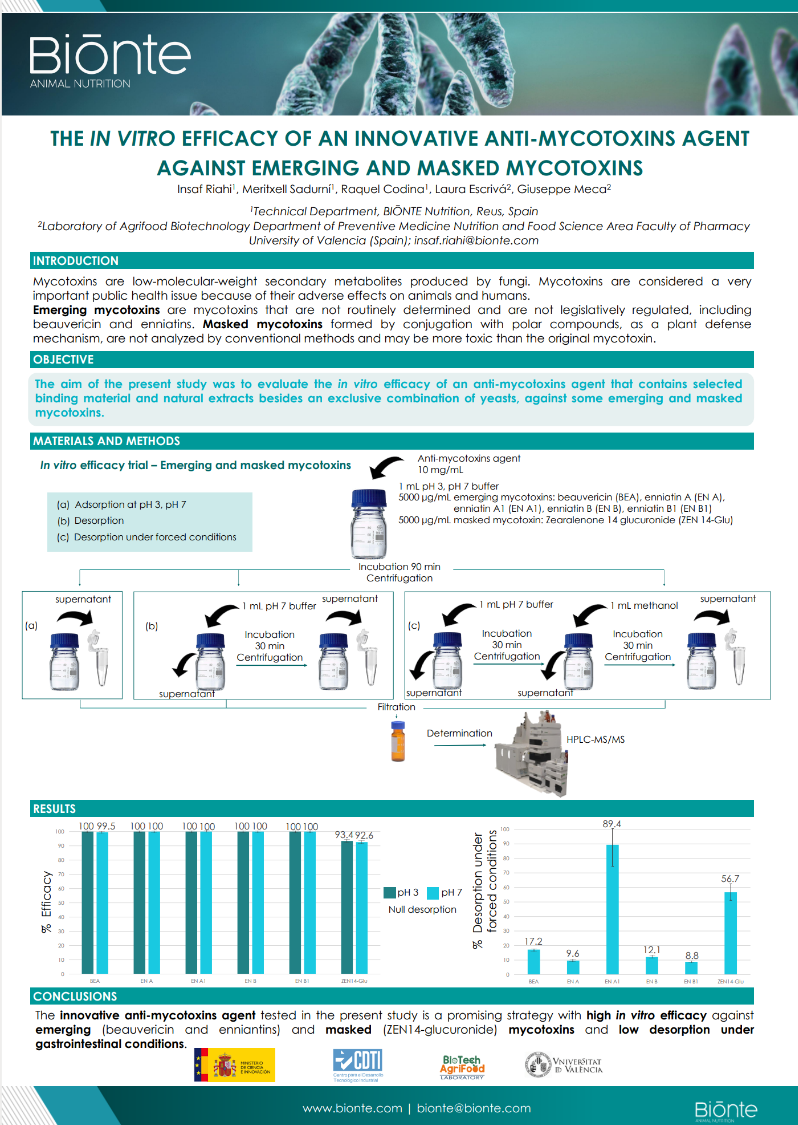
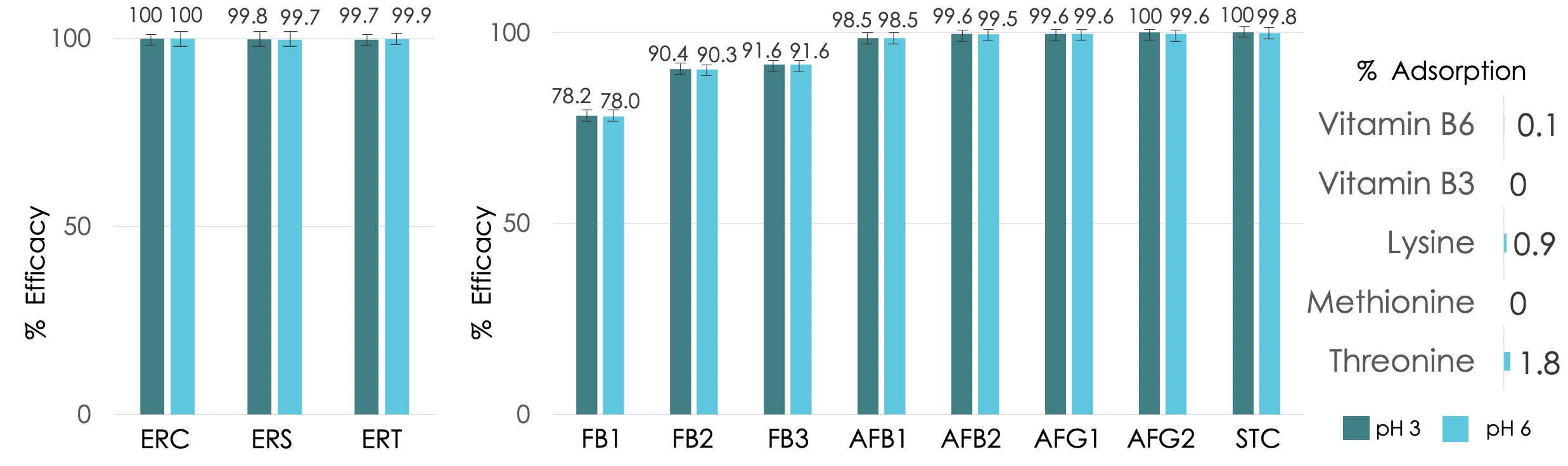
RESULTS
CONCLUSIONS
The anti-mycotoxins agent tested in this study is selective and has a high efficacy to mitigate the ergot alkaloids, fumonisins, aflatoxins and STC, being a promising strategy to reduce the negative impact of mycotoxins.